SSL certificate make an encrypted connection and lay out trust and build relations.
One of the main parts of online business is establishing a trustworthy environment, where any potential clients feel confident about making a purchase. SSL certificate make a reinforcement of trust by establishing a secure connection. To guarantee users about their connection is secure. Browser give extraordinary visual cues that we call EV indicators – anything from a green padlock to branded URL bar.
HOW DOES IT WORKS?
SSL certificates provides a pair of keys i.e.: a public key and a private key. These keys work with each other and establish an encrypted connection. The certificate also contains “subject,” which is the identity of the certificate.
To get certification, you should create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This interaction makes a private key and public key on your server. The CSR data record that you send to the SSL Certificate issuer that’s called a Certificate Authority. Certificate Authority contains the public key. The CA utilizes the CSR data document to make a data structure to match your private key without compromising the actual key. The CA never sees the private key.
SSL certificate?
When you get the SSL certificate, you install it on your server. You likewise install an intermediary certificate that establishes credibility of your SSL certificate. It binds it to your CA’s root certificate. The guidelines for installation and testing your certificate will be different that depends upon your server.
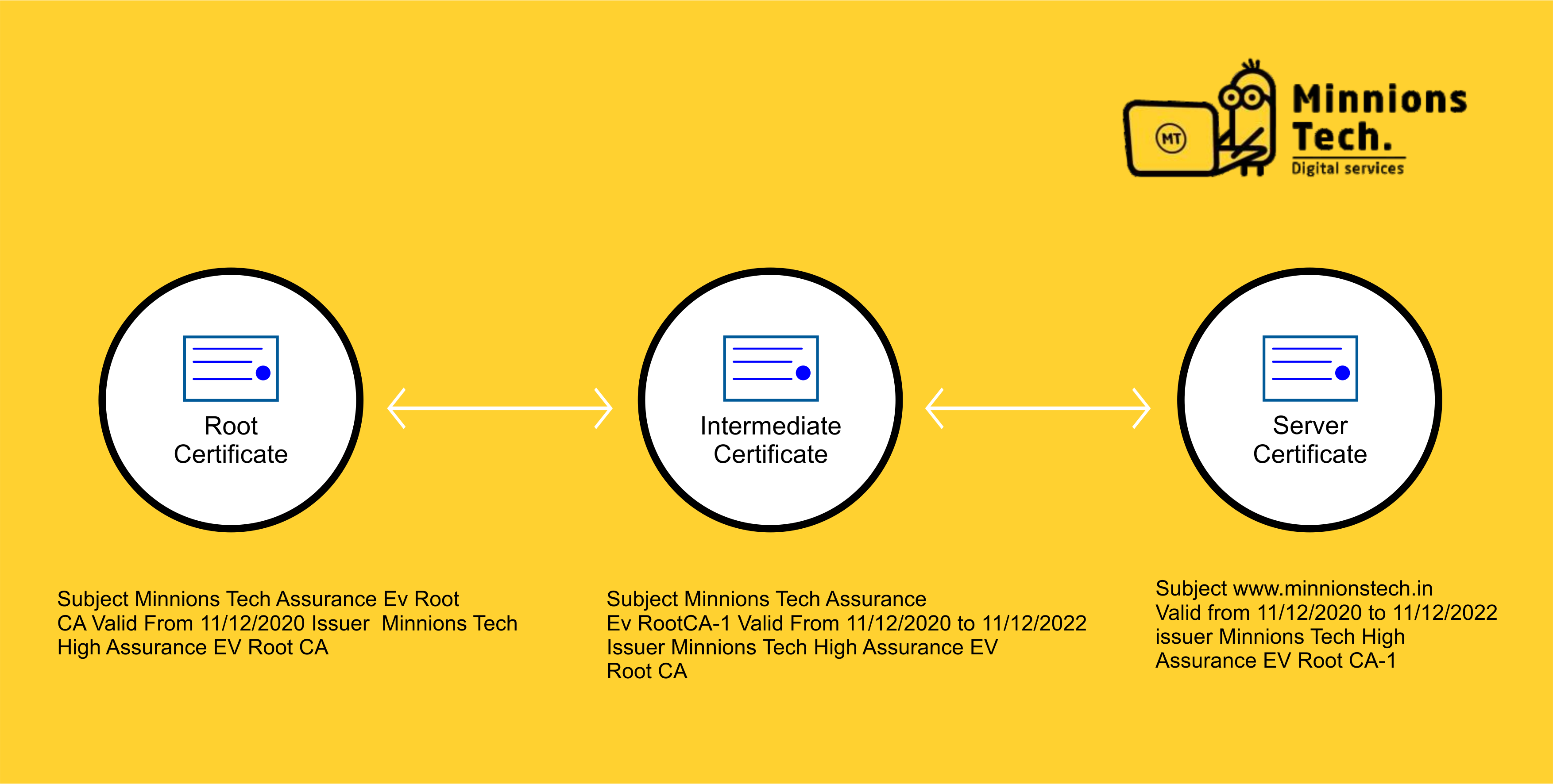
In the picture below, you can see what is certification chain. It interfaces your server certificate to the CA’s root certificate through an intermediate certificate.
The main part of an SSL certificate is that it is digitally endorsed by a trusted CA, as DigiCert. Anybody can make a certificate. Yet browser only trust certificate that come from an association on their list of trusted CAs. Browser accompany a pre-installed list of trusted CAs, known as the Trusted Root CA store. The order to be added as the Trusted Root CA store and hence become a Certificate Authority. An organization should compile with and be examined against security and verification principles established by the browser.
An SSL certificate issued by a CA to an association and its domain. Website checks a trusted third party has validated that association’s identity. Since the browser believes the CA, the browser now also believes that association’s identity as well. The browser tells the user that the website is secure. The visitor can have a real sense of safe browsing the website and even entering their confidential data.
WHAT IS SECURE SOCKETS LAYER (SSL)?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted interface between a server and a client. A web server generally called website and a browser, or a mail server and a mail client e.g., Outlook. It is more well-known than TLS, or Transport Layer Security, the successor technology of SSL.
SSL permits sensitive data, for example, credit card numbers, social security numbers, and login credentials to be sent safely. Typically, data sent among browser and web servers is sent in simple message – leaving you vulnerable to eavesdropping. Assuming an attacker can block all data being sent between a browser and a web server. They can see and utilize that data.
Although, SSL is a security protocol for any website. Protocol depict how algorithm ought to be utilized. For this situation, the SSL protocol decides factors of the encryption for both the link and the data being sent.
All browsers have the capacity to communicate with secured web servers using the SSL protocol. However, the browser and the server need to have the option to establish a solid secure connection.
SSL secures a large number of people groups’ their data on the Internet every day. Particularly during online exchanges or while sending confidential data. Web users have come to connect their online security with the lock symbol. It accompanies an SSL- secured site, or green address bar that accompanies an Extended Validation SSL-secured website. SSL- secured sites additionally start with “https” rather than “http.”
As of now comprehend the basics of SSL certificate and technology? Find out with regards to SSL here en.wikipedia.org.
HOW DOES THE SSL CERTIFICATE CREATE A SECURE CONNECTION?
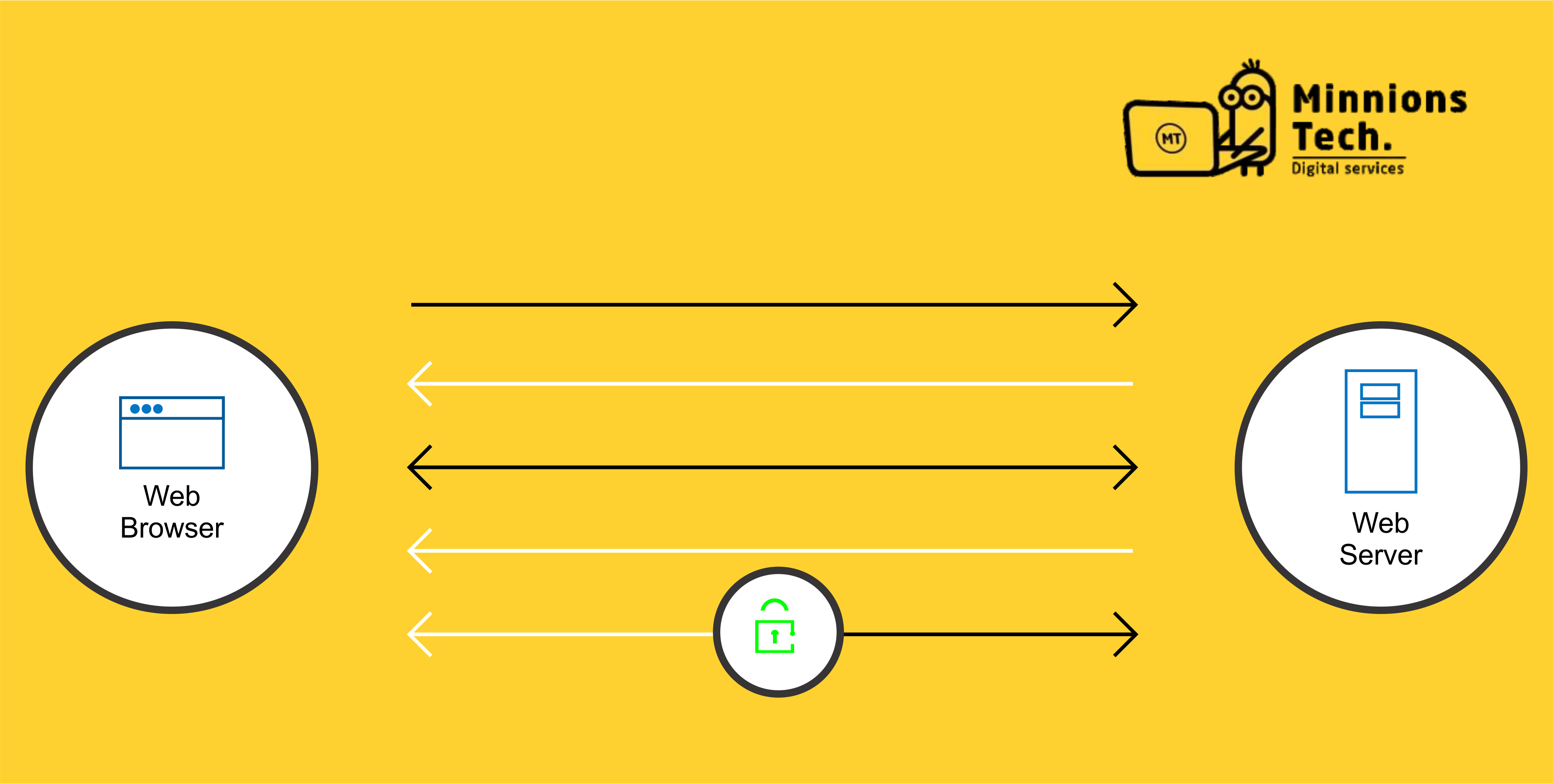
Whenever a browser endeavors to get access on a website that is secure by SSL. The browser and the web server establish an SSL interface, utilizing a method called an “SSL Handshake” (see pictures below). Note that the SSL Handshake is not visible to the visitor/users and happens immediately.
Basically, three keys are used to set up the SSL certificate: the public, private, and session keys. Anything scrambled with the public key must be decrypted with the private key, and vice-versa. Since encoding and decoding with private and public key takes a ton of processing power. They just used during the SSL Handshake to make a symmetric session key. After the safe symmetric session is over, the session key encrypt every sent information.
- Browser associates with a web server secured with SSL (https). Browser demands that the server distinguish itself.
- Server sends a copy of its SSL Certificate, including the server’s public key.
- Browser checks the certificate root against a rundown of trusted CAs and that the certificate is unexpired, unrevoked. That its common name is substantial for the website that it is interfacing with. If the browser believes the certificate, it makes, scrambles, and sends back a symmetric session key. This utilizing the server’s public key.
- Server decodes the symmetric session key utilizing its private key. Then it sends back an affirmation encrypted with the session key to begin the encrypted meeting.
- Server and Browser presently encrypt all transmitted information with the session key.
IS MY CERTIFICATE SSL OR TLS?
The SSL protocol has been use to all of the time to encrypt and secure sent information. Each time a new and safer version was releases for certification. Just the version number was alter to reflect the change (e.g., SSLv2.0). However, when the time arrived to refresh from SSLv3.0, rather than calling the new version SSLv4.0, it was rename to TLSv1.0. We are presently on TLSv1.3.
Since SSL is as yet the better known, more commonly utilized term.
USES OF TLS AND SSL CERTIFICATE
| Uses | Informational sites & blogs
Websites that don’t collect payments or sensitive information need HTTPS to keep user activity private-even blogs. |
Login panels & forms
TLS/SSL encrypts and protects usernames and passwords, as well as forms used to submit personal information, documents or images. |
Checkout pages
Customers are more likely to complete a purchase if they know, your checkout area is secure. |
| Recommended TLS/SSL Certificate | Organization Validated TLS/SSL certificates –
The second highest level of authenticity and next most rigorous organization checks. |
Organization Validated TLS/SSL certificates –
The second highest level of authenticity and most-rigorous organization checks. |
Extended Validation TLS/SSL Certificates –
The highest level of authenticity and most-rigorous identity checks. |
| DigiCert Products | DigiCert Secure Site or
Basic |
DigiCert Secure Site | DigiCert Secure Site Pro |
LOOK BEYOND THE LOCK
Simply seeing a lock in the address bar is now not sufficient. By tapping on the lock symbol in the URL bar you can verify the security and identity of the site owner.
Sadly, most phishing website today have a padlock and a DV authentication certificate. That is the reason it’s very essential to look beyond the lock in the URL bar. If the website isn’t willing to place their identity in the certification, you shouldn’t impart any identifying data to them. Suppose if you see the company name, then you can settle on a superior choice with regards to who you trust.